这篇文章上次修改于 276 天前,可能其部分内容已经发生变化,如有疑问可询问作者。
前言
在开始这篇文章之前,我们得首先弄明白,什么是图像分割?
我们知道一个图像只不过是许多像素的集合。图像分割分类是对图像中属于特定类别的像素进行分类的过程,即像素级别的下游任务。因此图像分割简单来说就是按像素进行分类的问题。
传统的图像分割算法均是基于灰度值的不连续和相似的性质。而基于深度学习的图像分割技术则是利用卷积神经网络,来理解图像中的每个像素所代表的真实世界物体,这在以前是难以想象的。

语义分割(Semantic Segmentation)
** 定义**
“语义”是个很抽象的概念,在 2D 图像领域,每个像素点作为最小单位,它的像素值代表的就是一个特征,即“语义”信息。语义分割会为图像中的每个像素分配一个类别,但是同一类别之间的对象不会区分。而实例分割,只对特定的物体进行分类。这看起来与目标检测相似,不同的是目标检测输出目标的边界框和类别,实例分割输出的是目标的 Mask 和类别。具体而言,语义分割的目的是为了从像素级别理解图像的内容,并为图像中的每个像素分配一个对象类。
语义分割是一种将图像中的每个像素分配给特定类别的技术。其目标是识别图像中存在的各种对象和背景,并为每个像素分配相应的类别标签。例如,将图像中的像素划分为人、树、草地和天空等不同区域。是图像处理和机器视觉一个重要分支。与分类任务不同,语义分割需要判断图像每个像素点的类别,进行精确分割。语义分割目前在自动驾驶、自动抠图、医疗影像等领域有着比较广泛的应用。
** 特点**
- 提供精确的像素级分类,有助于深入理解图像内容。
- 无法区分同一类别中的不同实例。
** 语义分割的应用**
语义分割在多个领域有广泛应用:
- 自动驾驶:用于道路、车辆和行人的识别。
- 医学成像:用于组织和器官的分割。
- 卫星遥感:用于土地覆盖分类。
** 常见模型**
FCN(Fully Convolutional Network)
- 优点:简单易用,但是现在已经很少使用了,但它的历史贡献不可忽视。
- 缺点:分割精度较低,可能无法很好地处理细节。
提出初衷

FCN(全卷积网络)模型的初衷是为了解决传统卷积神经网络(CNN)在语义分割任务中的局限性。具体而言,传统 CNN 使用全连接层进行分类,这会丢失图像的空间位置信息,导致其不适合像素级的预测任务。FCN 的核心动机包括:
- 实现端到端的像素级预测:FCN 通过将全连接层替换为卷积层,使得网络能够接受任意尺寸的输入图像,并输出与输入尺寸相同的像素级预测结果。
- 保留空间信息:取消全连接层后,FCN 能够保留图像的空间位置信息,从而更好地适应语义分割任务。
- 提高分割效率和精度:通过引入反卷积层(上采样层)和跳跃连接(Skip Connections),FCN 能够融合不同深度的特征,兼顾全局语义信息和局部细节,从而提升分割精度。
- 利用预训练模型加速训练:FCN 可以基于预训练的分类模型(如 AlexNet、VGG 等)进行微调,从而显著加速训练过程并提高模型性能。
网络结构
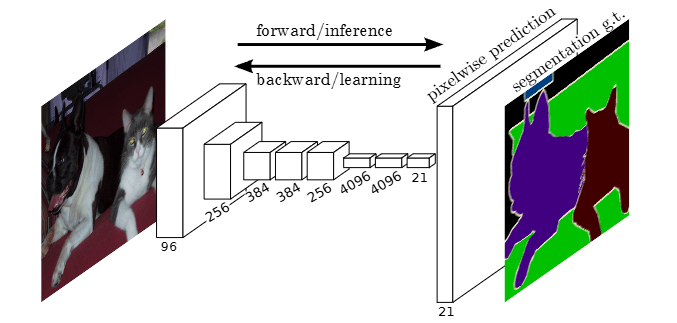
通常 CNN 网络在卷积层之后会接上若干个全连接层, 将卷积层产生的特征图(feature map)映射成一个固定长度的特征向量。以 AlexNet 为代表的经典 CNN 结构适合于图像级的分类和回归任务,因为它们最后都期望得到整个输入图像的一个数值描述(概率)。
FCN 对图像进行像素级的分类,从而解决了语义级别的图像分割(semantic segmentation)问题。与经典的 CNN 在卷积层之后使用全连接层得到固定长度的特征向量进行分类(全连接层 +softmax 输出)不同,FCN 可以接受任意尺寸的输入图像,采用反卷积层对最后一个卷积层的 feature map 进行上采样, 使它恢复到输入图像相同的尺寸,从而可以对每个像素都产生了一个预测, 同时保留了原始输入图像中的空间信息, 最后在上采样的特征图上进行逐像素分类。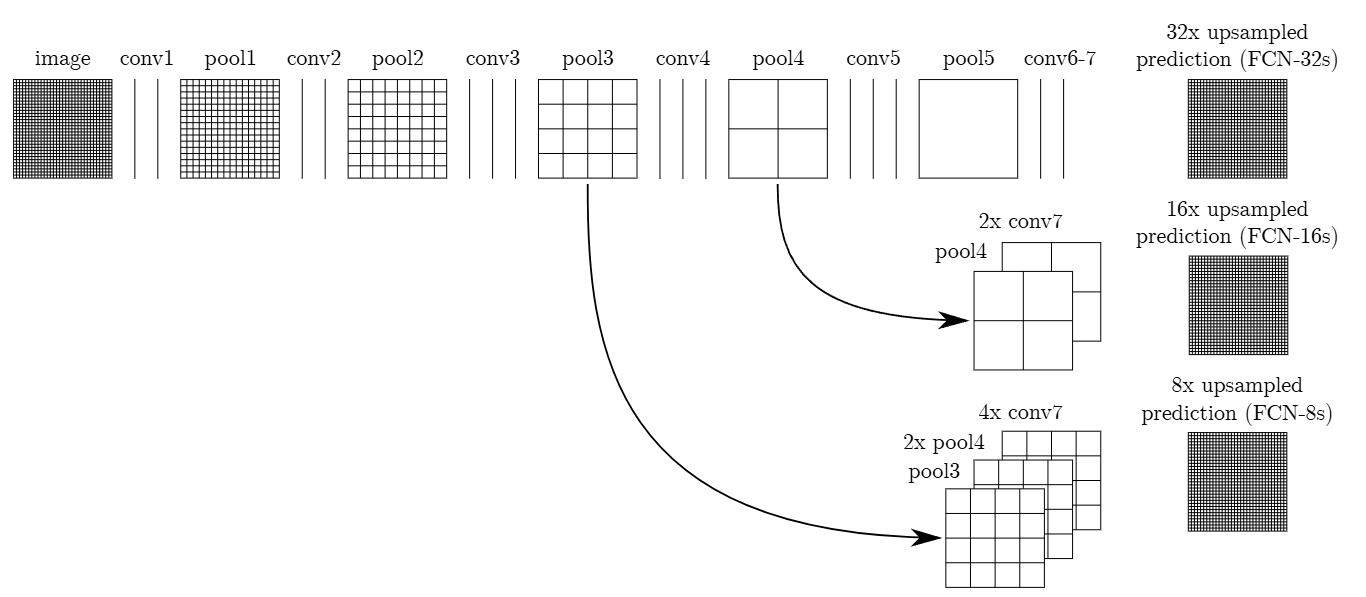
FCN(全卷积网络)为了解决语义分割(semantic segmentation)问题而提出,它对图像进行像素级的分类,能够保留原始输入图像中的空间信息。与传统 CNN 不同,FCN 可以接受任意尺寸的输入图像,并通过以下方式实现像素级分类:
- 去除全连接层:FCN 将传统 CNN 中的全连接层替换为卷积层,从而保留空间信息。
- 上采样操作:使用反卷积层(上采样层)对最后一个卷积层的特征图进行上采样,恢复到与输入图像相同的尺寸。
- 逐像素分类:在上采样后的特征图上进行逐像素分类,为每个像素生成类别预测。
Q:FCN 是如何通过上采样操作恢复特征图的空间分辨率的?
模型代码
论文源码
import caffe
from caffe import layers as L, params as P
from caffe.coord_map import crop
def conv_relu(bottom, nout, ks=3, stride=1, pad=1):
conv = L.Convolution(bottom, kernel_size=ks, stride=stride,
num_output=nout, pad=pad,
param=[dict(lr_mult=1, decay_mult=1), dict(lr_mult=2, decay_mult=0)])
return conv, L.ReLU(conv, in_place=True)
def max_pool(bottom, ks=2, stride=2):
return L.Pooling(bottom, pool=P.Pooling.MAX, kernel_size=ks, stride=stride)
def fcn(split):
n = caffe.NetSpec()
pydata_params = dict(split=split, mean=(104.00699, 116.66877, 122.67892),
seed=1337)
if split == 'train':
pydata_params['sbdd_dir'] = '../data/sbdd/dataset'
pylayer = 'SBDDSegDataLayer'
else:
pydata_params['voc_dir'] = '../data/pascal/VOC2011'
pylayer = 'VOCSegDataLayer'
n.data, n.label = L.Python(module='voc_layers', layer=pylayer,
ntop=2, param_str=str(pydata_params))
# the base net
n.conv1_1, n.relu1_1 = conv_relu(n.data, 64, pad=100)
n.conv1_2, n.relu1_2 = conv_relu(n.relu1_1, 64)
n.pool1 = max_pool(n.relu1_2)
n.conv2_1, n.relu2_1 = conv_relu(n.pool1, 128)
n.conv2_2, n.relu2_2 = conv_relu(n.relu2_1, 128)
n.pool2 = max_pool(n.relu2_2)
n.conv3_1, n.relu3_1 = conv_relu(n.pool2, 256)
n.conv3_2, n.relu3_2 = conv_relu(n.relu3_1, 256)
n.conv3_3, n.relu3_3 = conv_relu(n.relu3_2, 256)
n.pool3 = max_pool(n.relu3_3)
n.conv4_1, n.relu4_1 = conv_relu(n.pool3, 512)
n.conv4_2, n.relu4_2 = conv_relu(n.relu4_1, 512)
n.conv4_3, n.relu4_3 = conv_relu(n.relu4_2, 512)
n.pool4 = max_pool(n.relu4_3)
n.conv5_1, n.relu5_1 = conv_relu(n.pool4, 512)
n.conv5_2, n.relu5_2 = conv_relu(n.relu5_1, 512)
n.conv5_3, n.relu5_3 = conv_relu(n.relu5_2, 512)
n.pool5 = max_pool(n.relu5_3)
# fully conv
n.fc6, n.relu6 = conv_relu(n.pool5, 4096, ks=7, pad=0)
n.drop6 = L.Dropout(n.relu6, dropout_ratio=0.5, in_place=True)
n.fc7, n.relu7 = conv_relu(n.drop6, 4096, ks=1, pad=0)
n.drop7 = L.Dropout(n.relu7, dropout_ratio=0.5, in_place=True)
n.score_fr = L.Convolution(n.drop7, num_output=21, kernel_size=1, pad=0,
param=[dict(lr_mult=1, decay_mult=1), dict(lr_mult=2, decay_mult=0)])
n.upscore2 = L.Deconvolution(n.score_fr,
convolution_param=dict(num_output=21, kernel_size=4, stride=2,
bias_term=False),
param=[dict(lr_mult=0)])
n.score_pool4 = L.Convolution(n.pool4, num_output=21, kernel_size=1, pad=0,
param=[dict(lr_mult=1, decay_mult=1), dict(lr_mult=2, decay_mult=0)])
n.score_pool4c = crop(n.score_pool4, n.upscore2)
n.fuse_pool4 = L.Eltwise(n.upscore2, n.score_pool4c,
operation=P.Eltwise.SUM)
n.upscore_pool4 = L.Deconvolution(n.fuse_pool4,
convolution_param=dict(num_output=21, kernel_size=4, stride=2,
bias_term=False),
param=[dict(lr_mult=0)])
n.score_pool3 = L.Convolution(n.pool3, num_output=21, kernel_size=1, pad=0,
param=[dict(lr_mult=1, decay_mult=1), dict(lr_mult=2, decay_mult=0)])
n.score_pool3c = crop(n.score_pool3, n.upscore_pool4)
n.fuse_pool3 = L.Eltwise(n.upscore_pool4, n.score_pool3c,
operation=P.Eltwise.SUM)
n.upscore8 = L.Deconvolution(n.fuse_pool3,
convolution_param=dict(num_output=21, kernel_size=16, stride=8,
bias_term=False),
param=[dict(lr_mult=0)])
n.score = crop(n.upscore8, n.data)
n.loss = L.SoftmaxWithLoss(n.score, n.label,
loss_param=dict(normalize=False, ignore_label=255))
return n.to_proto()
def make_net():
with open('train.prototxt', 'w') as f:
f.write(str(fcn('train')))
with open('val.prototxt', 'w') as f:
f.write(str(fcn('seg11valid')))
if __name__ == '__main__':
make_net()fcn8_vgg
from __future__ import absolute_import
from __future__ import division
from __future__ import print_function
import os
import logging
from math import ceil
import sys
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
VGG_MEAN = [103.939, 116.779, 123.68]
class FCN8VGG:
def __init__(self, vgg16_npy_path=None):
if vgg16_npy_path is None:
path = sys.modules[self.__class__.__module__].__file__
# print path
path = os.path.abspath(os.path.join(path, os.pardir))
# print path
path = os.path.join(path, "vgg16.npy")
vgg16_npy_path = path
logging.info("Load npy file from '%s'.", vgg16_npy_path)
if not os.path.isfile(vgg16_npy_path):
logging.error(("File '%s' not found. Download it from "
"ftp://mi.eng.cam.ac.uk/pub/mttt2/"
"models/vgg16.npy"), vgg16_npy_path)
sys.exit(1)
self.data_dict = np.load(vgg16_npy_path, encoding='latin1').item()
self.wd = 5e-4
print("npy file loaded")
def build(self, rgb, train=False, num_classes=20, random_init_fc8=False,
debug=False, use_dilated=False):
"""
Build the VGG model using loaded weights
Parameters
----------
rgb: image batch tensor
Image in rgb shap. Scaled to Intervall [0, 255]
train: bool
Whether to build train or inference graph
num_classes: int
How many classes should be predicted (by fc8)
random_init_fc8 : bool
Whether to initialize fc8 layer randomly.
Finetuning is required in this case.
debug: bool
Whether to print additional Debug Information.
"""
# Convert RGB to BGR
with tf.name_scope('Processing'):
red, green, blue = tf.split(rgb, 3, 3)
# assert red.get_shape().as_list()[1:] == [224, 224, 1]
# assert green.get_shape().as_list()[1:] == [224, 224, 1]
# assert blue.get_shape().as_list()[1:] == [224, 224, 1]
bgr = tf.concat([
blue - VGG_MEAN[0],
green - VGG_MEAN[1],
red - VGG_MEAN[2],
], 3)
if debug:
bgr = tf.Print(bgr, [tf.shape(bgr)],
message='Shape of input image: ',
summarize=4, first_n=1)
self.conv1_1 = self._conv_layer(bgr, "conv1_1")
self.conv1_2 = self._conv_layer(self.conv1_1, "conv1_2")
self.pool1 = self._max_pool(self.conv1_2, 'pool1', debug)
self.conv2_1 = self._conv_layer(self.pool1, "conv2_1")
self.conv2_2 = self._conv_layer(self.conv2_1, "conv2_2")
self.pool2 = self._max_pool(self.conv2_2, 'pool2', debug)
self.conv3_1 = self._conv_layer(self.pool2, "conv3_1")
self.conv3_2 = self._conv_layer(self.conv3_1, "conv3_2")
self.conv3_3 = self._conv_layer(self.conv3_2, "conv3_3")
self.pool3 = self._max_pool(self.conv3_3, 'pool3', debug)
self.conv4_1 = self._conv_layer(self.pool3, "conv4_1")
self.conv4_2 = self._conv_layer(self.conv4_1, "conv4_2")
self.conv4_3 = self._conv_layer(self.conv4_2, "conv4_3")
if use_dilated:
pad = [[0, 0], [0, 0]]
self.pool4 = tf.nn.max_pool(self.conv4_3, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1],
strides=[1, 1, 1, 1],
padding='SAME', name='pool4')
self.pool4 = tf.space_to_batch(self.pool4,
paddings=pad, block_size=2)
else:
self.pool4 = self._max_pool(self.conv4_3, 'pool4', debug)
self.conv5_1 = self._conv_layer(self.pool4, "conv5_1")
self.conv5_2 = self._conv_layer(self.conv5_1, "conv5_2")
self.conv5_3 = self._conv_layer(self.conv5_2, "conv5_3")
if use_dilated:
pad = [[0, 0], [0, 0]]
self.pool5 = tf.nn.max_pool(self.conv5_3, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1],
strides=[1, 1, 1, 1],
padding='SAME', name='pool5')
self.pool5 = tf.space_to_batch(self.pool5,
paddings=pad, block_size=2)
else:
self.pool5 = self._max_pool(self.conv5_3, 'pool5', debug)
self.fc6 = self._fc_layer(self.pool5, "fc6")
if train:
self.fc6 = tf.nn.dropout(self.fc6, 0.5)
self.fc7 = self._fc_layer(self.fc6, "fc7")
if train:
self.fc7 = tf.nn.dropout(self.fc7, 0.5)
if use_dilated:
self.pool5 = tf.batch_to_space(self.pool5, crops=pad, block_size=2)
self.pool5 = tf.batch_to_space(self.pool5, crops=pad, block_size=2)
self.fc7 = tf.batch_to_space(self.fc7, crops=pad, block_size=2)
self.fc7 = tf.batch_to_space(self.fc7, crops=pad, block_size=2)
return
if random_init_fc8:
self.score_fr = self._score_layer(self.fc7, "score_fr",
num_classes)
else:
self.score_fr = self._fc_layer(self.fc7, "score_fr",
num_classes=num_classes,
relu=False)
self.pred = tf.argmax(self.score_fr, dimension=3)
self.upscore2 = self._upscore_layer(self.score_fr,
shape=tf.shape(self.pool4),
num_classes=num_classes,
debug=debug, name='upscore2',
ksize=4, stride=2)
self.score_pool4 = self._score_layer(self.pool4, "score_pool4",
num_classes=num_classes)
self.fuse_pool4 = tf.add(self.upscore2, self.score_pool4)
self.upscore4 = self._upscore_layer(self.fuse_pool4,
shape=tf.shape(self.pool3),
num_classes=num_classes,
debug=debug, name='upscore4',
ksize=4, stride=2)
self.score_pool3 = self._score_layer(self.pool3, "score_pool3",
num_classes=num_classes)
self.fuse_pool3 = tf.add(self.upscore4, self.score_pool3)
self.upscore32 = self._upscore_layer(self.fuse_pool3,
shape=tf.shape(bgr),
num_classes=num_classes,
debug=debug, name='upscore32',
ksize=16, stride=8)
self.pred_up = tf.argmax(self.upscore32, dimension=3)
def _max_pool(self, bottom, name, debug):
pool = tf.nn.max_pool(bottom, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1],
padding='SAME', name=name)
if debug:
pool = tf.Print(pool, [tf.shape(pool)],
message='Shape of %s' % name,
summarize=4, first_n=1)
return pool
def _conv_layer(self, bottom, name):
with tf.variable_scope(name) as scope:
filt = self.get_conv_filter(name)
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(bottom, filt, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
conv_biases = self.get_bias(name)
bias = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, conv_biases)
relu = tf.nn.relu(bias)
# Add summary to Tensorboard
_activation_summary(relu)
return relu
def _fc_layer(self, bottom, name, num_classes=None,
relu=True, debug=False):
with tf.variable_scope(name) as scope:
shape = bottom.get_shape().as_list()
if name == 'fc6':
filt = self.get_fc_weight_reshape(name, [7, 7, 512, 4096])
elif name == 'score_fr':
name = 'fc8' # Name of score_fr layer in VGG Model
filt = self.get_fc_weight_reshape(name, [1, 1, 4096, 1000],
num_classes=num_classes)
else:
filt = self.get_fc_weight_reshape(name, [1, 1, 4096, 4096])
self._add_wd_and_summary(filt, self.wd, "fc_wlosses")
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(bottom, filt, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
conv_biases = self.get_bias(name, num_classes=num_classes)
bias = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, conv_biases)
if relu:
bias = tf.nn.relu(bias)
_activation_summary(bias)
if debug:
bias = tf.Print(bias, [tf.shape(bias)],
message='Shape of %s' % name,
summarize=4, first_n=1)
return bias
def _score_layer(self, bottom, name, num_classes):
with tf.variable_scope(name) as scope:
# get number of input channels
in_features = bottom.get_shape()[3].value
shape = [1, 1, in_features, num_classes]
# He initialization Sheme
if name == "score_fr":
num_input = in_features
stddev = (2 / num_input)**0.5
elif name == "score_pool4":
stddev = 0.001
elif name == "score_pool3":
stddev = 0.0001
# Apply convolution
w_decay = self.wd
weights = self._variable_with_weight_decay(shape, stddev, w_decay,
decoder=True)
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(bottom, weights, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
# Apply bias
conv_biases = self._bias_variable([num_classes], constant=0.0)
bias = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, conv_biases)
_activation_summary(bias)
return bias
def _upscore_layer(self, bottom, shape,
num_classes, name, debug,
ksize=4, stride=2):
strides = [1, stride, stride, 1]
with tf.variable_scope(name):
in_features = bottom.get_shape()[3].value
if shape is None:
# Compute shape out of Bottom
in_shape = tf.shape(bottom)
h = ((in_shape[1] - 1) * stride) + 1
w = ((in_shape[2] - 1) * stride) + 1
new_shape = [in_shape[0], h, w, num_classes]
else:
new_shape = [shape[0], shape[1], shape[2], num_classes]
output_shape = tf.stack(new_shape)
logging.debug("Layer: %s, Fan-in: %d" % (name, in_features))
f_shape = [ksize, ksize, num_classes, in_features]
# create
num_input = ksize * ksize * in_features / stride
stddev = (2 / num_input)**0.5
weights = self.get_deconv_filter(f_shape)
self._add_wd_and_summary(weights, self.wd, "fc_wlosses")
deconv = tf.nn.conv2d_transpose(bottom, weights, output_shape,
strides=strides, padding='SAME')
if debug:
deconv = tf.Print(deconv, [tf.shape(deconv)],
message='Shape of %s' % name,
summarize=4, first_n=1)
_activation_summary(deconv)
return deconv
def get_deconv_filter(self, f_shape):
width = f_shape[0]
height = f_shape[1]
f = ceil(width/2.0)
c = (2 * f - 1 - f % 2) / (2.0 * f)
bilinear = np.zeros([f_shape[0], f_shape[1]])
for x in range(width):
for y in range(height):
value = (1 - abs(x / f - c)) * (1 - abs(y / f - c))
bilinear[x, y] = value
weights = np.zeros(f_shape)
for i in range(f_shape[2]):
weights[:, :, i, i] = bilinear
init = tf.constant_initializer(value=weights,
dtype=tf.float32)
var = tf.get_variable(name="up_filter", initializer=init,
shape=weights.shape)
return var
def get_conv_filter(self, name):
init = tf.constant_initializer(value=self.data_dict[name][0],
dtype=tf.float32)
shape = self.data_dict[name][0].shape
print('Layer name: %s' % name)
print('Layer shape: %s' % str(shape))
var = tf.get_variable(name="filter", initializer=init, shape=shape)
if not tf.get_variable_scope().reuse:
weight_decay = tf.multiply(tf.nn.l2_loss(var), self.wd,
name='weight_loss')
tf.add_to_collection(tf.GraphKeys.REGULARIZATION_LOSSES,
weight_decay)
_variable_summaries(var)
return var
def get_bias(self, name, num_classes=None):
bias_wights = self.data_dict[name][1]
shape = self.data_dict[name][1].shape
if name == 'fc8':
bias_wights = self._bias_reshape(bias_wights, shape[0],
num_classes)
shape = [num_classes]
init = tf.constant_initializer(value=bias_wights,
dtype=tf.float32)
var = tf.get_variable(name="biases", initializer=init, shape=shape)
_variable_summaries(var)
return var
def get_fc_weight(self, name):
init = tf.constant_initializer(value=self.data_dict[name][0],
dtype=tf.float32)
shape = self.data_dict[name][0].shape
var = tf.get_variable(name="weights", initializer=init, shape=shape)
if not tf.get_variable_scope().reuse:
weight_decay = tf.multiply(tf.nn.l2_loss(var), self.wd,
name='weight_loss')
tf.add_to_collection(tf.GraphKeys.REGULARIZATION_LOSSES,
weight_decay)
_variable_summaries(var)
return var
def _bias_reshape(self, bweight, num_orig, num_new):
""" Build bias weights for filter produces with `_summary_reshape`
"""
n_averaged_elements = num_orig//num_new
avg_bweight = np.zeros(num_new)
for i in range(0, num_orig, n_averaged_elements):
start_idx = i
end_idx = start_idx + n_averaged_elements
avg_idx = start_idx//n_averaged_elements
if avg_idx == num_new:
break
avg_bweight[avg_idx] = np.mean(bweight[start_idx:end_idx])
return avg_bweight
def _summary_reshape(self, fweight, shape, num_new):
""" Produce weights for a reduced fully-connected layer.
FC8 of VGG produces 1000 classes. Most semantic segmentation
task require much less classes. This reshapes the original weights
to be used in a fully-convolutional layer which produces num_new
classes. To archive this the average (mean) of n adjanced classes is
taken.
Consider reordering fweight, to perserve semantic meaning of the
weights.
Args:
fweight: original weights
shape: shape of the desired fully-convolutional layer
num_new: number of new classes
Returns:
Filter weights for `num_new` classes.
"""
num_orig = shape[3]
shape[3] = num_new
assert(num_new < num_orig)
n_averaged_elements = num_orig//num_new
avg_fweight = np.zeros(shape)
for i in range(0, num_orig, n_averaged_elements):
start_idx = i
end_idx = start_idx + n_averaged_elements
avg_idx = start_idx//n_averaged_elements
if avg_idx == num_new:
break
avg_fweight[:, :, :, avg_idx] = np.mean(
fweight[:, :, :, start_idx:end_idx], axis=3)
return avg_fweight
def _variable_with_weight_decay(self, shape, stddev, wd, decoder=False):
"""Helper to create an initialized Variable with weight decay.
Note that the Variable is initialized with a truncated normal
distribution.
A weight decay is added only if one is specified.
Args:
name: name of the variable
shape: list of ints
stddev: standard deviation of a truncated Gaussian
wd: add L2Loss weight decay multiplied by this float. If None, weight
decay is not added for this Variable.
Returns:
Variable Tensor
"""
initializer = tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=stddev)
var = tf.get_variable('weights', shape=shape,
initializer=initializer)
collection_name = tf.GraphKeys.REGULARIZATION_LOSSES
if wd and (not tf.get_variable_scope().reuse):
weight_decay = tf.multiply(
tf.nn.l2_loss(var), wd, name='weight_loss')
tf.add_to_collection(collection_name, weight_decay)
_variable_summaries(var)
return var
def _add_wd_and_summary(self, var, wd, collection_name=None):
if collection_name is None:
collection_name = tf.GraphKeys.REGULARIZATION_LOSSES
if wd and (not tf.get_variable_scope().reuse):
weight_decay = tf.multiply(
tf.nn.l2_loss(var), wd, name='weight_loss')
tf.add_to_collection(collection_name, weight_decay)
_variable_summaries(var)
return var
def _bias_variable(self, shape, constant=0.0):
initializer = tf.constant_initializer(constant)
var = tf.get_variable(name='biases', shape=shape,
initializer=initializer)
_variable_summaries(var)
return var
def get_fc_weight_reshape(self, name, shape, num_classes=None):
print('Layer name: %s' % name)
print('Layer shape: %s' % shape)
weights = self.data_dict[name][0]
weights = weights.reshape(shape)
if num_classes is not None:
weights = self._summary_reshape(weights, shape,
num_new=num_classes)
init = tf.constant_initializer(value=weights,
dtype=tf.float32)
var = tf.get_variable(name="weights", initializer=init, shape=shape)
return var
def _activation_summary(x):
"""Helper to create summaries for activations.
Creates a summary that provides a histogram of activations.
Creates a summary that measure the sparsity of activations.
Args:
x: Tensor
Returns:
nothing
"""
# Remove 'tower_[0-9]/' from the name in case this is a multi-GPU training
# session. This helps the clarity of presentation on tensorboard.
tensor_name = x.op.name
# tensor_name = re.sub('%s_[0-9]*/' % TOWER_NAME, '', x.op.name)
tf.summary.histogram(tensor_name + '/activations', x)
tf.summary.scalar(tensor_name + '/sparsity', tf.nn.zero_fraction(x))
def _variable_summaries(var):
"""Attach a lot of summaries to a Tensor."""
if not tf.get_variable_scope().reuse:
name = var.op.name
logging.info("Creating Summary for: %s" % name)
with tf.name_scope('summaries'):
mean = tf.reduce_mean(var)
tf.summary.scalar(name + '/mean', mean)
with tf.name_scope('stddev'):
stddev = tf.sqrt(tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(var - mean)))
tf.summary.scalar(name + '/sttdev', stddev)
tf.summary.scalar(name + '/max', tf.reduce_max(var))
tf.summary.scalar(name + '/min', tf.reduce_min(var))
tf.summary.histogram(name, var)fcn 调包
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from abc import ABCMeta
import torchvision.models as models
def _maybe_pad(x, size):
hpad = size[0] - x.shape[2]
wpad = size[1] - x.shape[3]
if hpad + wpad > 0:
x = F.pad(x, (0, wpad, 0, hpad, 0, 0, 0, 0 ))
return x
class VGGFCN(nn.Module, metaclass=ABCMeta):
def __init__(self, in_channels, n_classes):
super().__init__()
assert in_channels == 3
self.n_classes = n_classes
self.vgg16 = models.vgg16(pretrained=True)
self.classifier = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(512, 4096, kernel_size=7, padding=3),
nn.ReLU(True),
nn.Dropout(),
nn.Conv2d(4096, 4096, kernel_size=1),
nn.ReLU(True),
nn.Dropout(),
nn.Conv2d(4096, n_classes, kernel_size=1),
)
self._initialize_weights()
def _initialize_weights(self):
self.classifier[0].weight.data = (
self.vgg16.classifier[0].weight.data.view(
self.classifier[0].weight.size())
)
self.classifier[3].weight.data = (
self.vgg16.classifier[3].weight.data.view(
self.classifier[3].weight.size())
)
class VGGFCN32(VGGFCN):
def forward(self, x):
input_height, input_width = x.shape[2], x.shape[3]
x = self.vgg16.features(x)
x = self.classifier(x)
x = F.interpolate(x, size=(input_height, input_width),
mode='bilinear', align_corners=True)
return x
class VGGFCN16(VGGFCN):
def __init__(self, in_channels, n_classes):
super().__init__(in_channels, n_classes)
self.score4 = nn.Conv2d(512, n_classes, kernel_size=1)
self.upscale5 = nn.ConvTranspose2d(
n_classes, n_classes, kernel_size=2, stride=2)
def forward(self, x):
input_height, input_width = x.shape[2], x.shape[3]
pool4 = self.vgg16.features[:-7](x)
pool5 = self.vgg16.features[-7:](pool4)
pool5_upscaled = self.upscale5(self.classifier(pool5))
pool4 = self.score4(pool4)
x = pool4 + pool5_upscaled
x = F.interpolate(x, size=(input_height, input_width),
mode='bilinear', align_corners=True)
return x
class VGGFCN8(VGGFCN):
def __init__(self, in_channels, n_classes):
super().__init__(in_channels, n_classes)
self.upscale4 = nn.ConvTranspose2d(
n_classes, n_classes, kernel_size=2, stride=2)
self.score4 = nn.Conv2d(
512, n_classes, kernel_size=1, stride=1)
self.score3 = nn.Conv2d(
256, n_classes, kernel_size=1, stride=1)
self.upscale5 = nn.ConvTranspose2d(
n_classes, n_classes, kernel_size=2, stride=2)
def forward(self, x):
input_height, input_width = x.shape[2], x.shape[3]
pool3 = self.vgg16.features[:-14](x)
pool4 = self.vgg16.features[-14:-7](pool3)
pool5 = self.vgg16.features[-7:](pool4)
pool5_upscaled = self.upscale5(self.classifier(pool5))
pool5_upscaled = _maybe_pad(pool5_upscaled, pool4.shape[2:])
pool4_scores = self.score4(pool4)
pool4_fused = pool4_scores + pool5_upscaled
pool4_upscaled = self.upscale4(pool4_fused)
pool4_upscaled = _maybe_pad(pool4_upscaled, pool3.shape[2:])
x = self.score3(pool3) + pool4_upscaled
x = F.interpolate(x, size=(input_height, input_width),
mode='bilinear', align_corners=True)
return x相关资源
U-Net
- 优点:简单易用,适用于小数据集,尤其在医学图像分割中表现良好。
- 缺点:容易过拟合,不太适合大规模数据集。
提出初衷
U-Net 是一种经典且广泛使用的分割模型,以其简单、高效、易于理解和构建的特点而受到青睐,尤其适合从小数据集中进行训练。该模型最早于 2015 年在论文《U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation》中被提出,至今仍然是医学图像分割领域的重要基础模型。
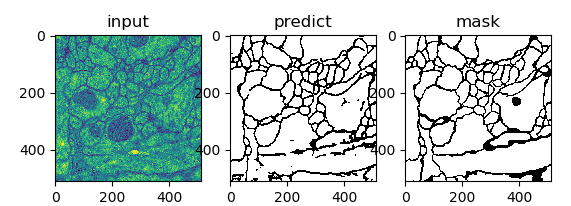
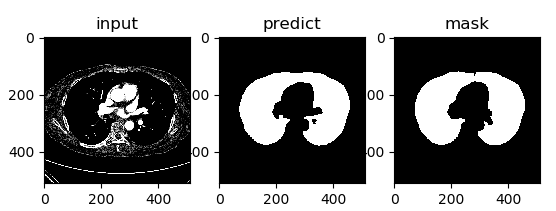
- Unet 提出的初衷是为了解决医学图像分割的问题;
- 一种 U 型的网络结构来获取上下文的信息和位置信息;
- 在 2015 年的 ISBI cell tracking 比赛中获得了多个第一,一开始这是为了解决细胞层面的分割的任务的
网络结构
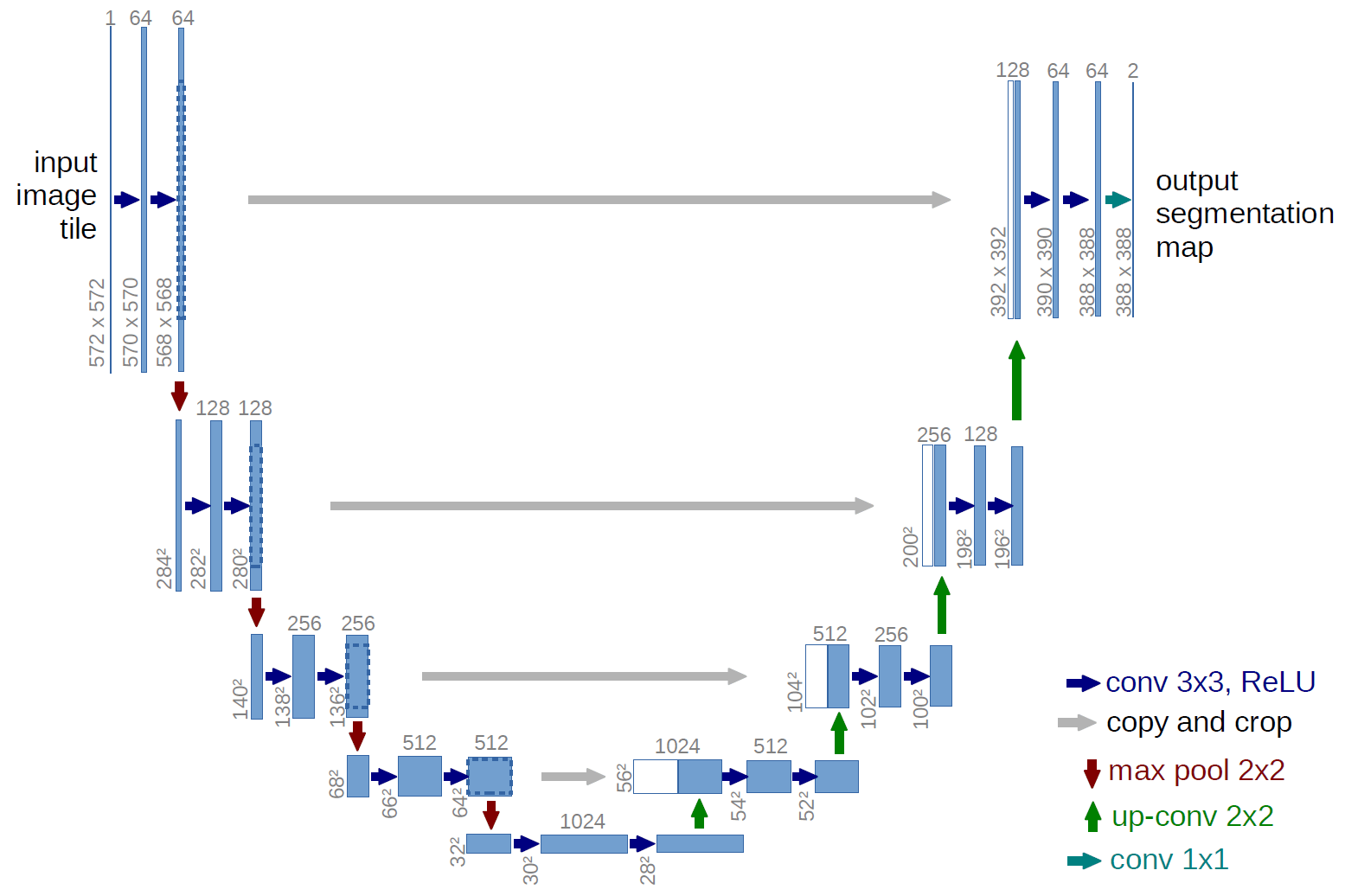
U-Net 网络是一种经典的编码器-解码器结构,因其整体结构形似大写的英文字母“U”而得名。它广泛应用于医学图像分割等领域。U-Net 的设计非常简洁:前半部分用于特征提取(编码器),后半部分用于上采样(解码器)。
编码器(Encoder)
编码器位于网络的左半部分,主要由多个下采样模块组成。每个模块包含两个 3×3 的卷积层(激活函数为 ReLU),后接一个 2×2 的最大池化(Max Pooling)层,用于特征提取和空间尺寸的减半。通过这种结构,编码器能够逐步提取图像的深层特征,同时扩大感受野。
解码器(Decoder)
解码器位于网络的右半部分,主要由上采样模块组成。每个模块包含一个 2×2 的反卷积层(上采样卷积层),用于将特征图的空间尺寸恢复到与编码器对应层相同的大小。随后,解码器通过特征拼接(concatenation)将上采样后的特征图与编码器中对应层的特征图进行通道级拼接,最后通过两个 3×3 的卷积层(激活函数为 ReLU)进一步融合特征。这种结构能够有效地结合深层特征和浅层特征,兼顾全局语义信息和局部细节。
特征融合方式
与 FCN 网络通过特征图对应像素值的相加来融合特征不同,U-Net 采用通道级拼接的方式。这种方式可以形成更厚的特征图,从而保留更多的细节信息,但也增加了显存的消耗。
U-Net 的优点
- 多尺度特征融合:U-Net 通过拼接深层和浅层特征图,能够充分利用不同层次的特征。浅层卷积关注纹理和细节特征,而深层网络关注更高级的语义特征。这种融合方式使得模型能够更好地处理复杂的分割任务。
- 边缘特征的保留:在下采样过程中,虽然会损失一些边缘特征,但通过特征拼接,解码器能够从编码器的浅层特征中找回这些丢失的边缘信息,从而提高分割的精度。
Unet 的好处我感觉是:网络层越深得到的特征图,有着更大的视野域,浅层卷积关注纹理特征,深层网络关注本质的那种特征,所以深层浅层特征都是有格子的意义的;另外一点是通过反卷积得到的更大的尺寸的特征图的边缘,是缺少信息的,毕竟每一次下采样提炼特征的同时,也必然会损失一些边缘特征,而失去的特征并不能从上采样中找回,因此通过特征的拼接,来实现边缘特征的一个找回。
下面是一些与医学相关的数据集以及对应的提取码,有兴趣的同学可以下载下来跑一下。
| **数据集名称** | **下载链接** | **提取码** |
| Cell dataset (dsb2018) | https://pan.baidu.com/share/init?surl=BaVrzYdrSP78CwYaRzZr1w | 5l54 |
| Liver dataset | https://pan.baidu.com/share/init?surl=FljGCVzu7HPYpwAKvSVN4Q | 5l88 |
| Cell dataset (isbi) | https://pan.baidu.com/share/init?surl=FkfnhU-RnYFZti62-f8AVA | 14rz |
| Lung dataset | https://pan.baidu.com/share/init?surl=sLFRmtG2TOTEgUKniJf7AA | qdwo |
| Corneal Nerve dataset | https://pan.baidu.com/share/init?surl=T3-kS_FgYI6DeXv3n1I7bA | ih02 |
| Eye Vessels (DRIVE dataset) | https://pan.baidu.com/share/init?surl=UkMLmdbM61N8ecgnKlAsPg | f1ek |
| Esophagus and Esophagus Cancer dataset (First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University) | https://pan.baidu.com/share/init?surl=0b5arIQjNpiggwdkgYNHXQ | hivm |
为什么 Unet 在医疗图像分割中表现好?
大多数医疗影像语义分割任务都会首先用 Unet 作为 baseline,当然上一章节讲解的 Unet 的优点肯定是可以当作这个问题的答案,这里谈一谈医疗影像的特点
根据网友的讨论,得到的结果:
- 医疗影像语义较为简单、结构固定。因此语义信息相比自动驾驶等较为单一,因此并不需要去筛选过滤无用的信息。医疗影像的所有特征都很重要,因此低级特征和高级语义特征都很重要,所以 U 型结构的 skip connection 结构(特征拼接)更好派上用场
- 医学影像的数据较少,获取难度大,数据量可能只有几百甚至不到 100,因此如果使用大型的网络例如 DeepLabv3+ 等模型,很容易过拟合。大型网络的优点是更强的图像表述能力,而较为简单、数量少的医学影像并没有那么多的内容需要表述,因此也有人发现在小数量级中,分割的 SOTA 模型与轻量的 Unet 并没有神恶魔优势
- 医学影像往往是多模态的。比方说 ISLES 脑梗竞赛中,官方提供了 CBF,MTT,CBV 等多中模态的数据(这一点听不懂也无妨)。因此医学影像任务中,往往需要自己设计网络去提取不同的模态特征,因此轻量结构简单的 Unet 可以有更大的操作空间。
Q:过拟合与模型复杂程度有关还和什么有关呢?
模型代码
源码
import torch.nn as nn
import torch
from torch import autograd
from functools import partial
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torchvision import models
class DoubleConv(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_ch, out_ch):
super(DoubleConv, self).__init__()
self.**conv** = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_ch, out_ch, 3, _padding_=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_ch),
nn.ReLU(_inplace_=True),
nn.Conv2d(out_ch, out_ch, 3, _padding_=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_ch),
nn.ReLU(_inplace_=True)
)
def forward(self, input):
return self.**conv**(input)
class Unet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_ch, out_ch):
super(Unet, self).__init__()
self.**conv1** = DoubleConv(in_ch, 32)
self.**pool1** = nn.MaxPool2d(2)
self.**conv2** = DoubleConv(32, 64)
self.**pool2** = nn.MaxPool2d(2)
self.**conv3** = DoubleConv(64, 128)
self.**pool3** = nn.MaxPool2d(2)
self.**conv4** = DoubleConv(128, 256)
self.**pool4** = nn.MaxPool2d(2)
self.**conv5** = DoubleConv(256, 512)
self.**up6** = nn.ConvTranspose2d(512, 256, 2, _stride_=2)
self.**conv6** = DoubleConv(512, 256)
self.**up7** = nn.ConvTranspose2d(256, 128, 2, _stride_=2)
self.**conv7** = DoubleConv(256, 128)
self.**up8** = nn.ConvTranspose2d(128, 64, 2, _stride_=2)
self.**conv8** = DoubleConv(128, 64)
self.**up9** = nn.ConvTranspose2d(64, 32, 2, _stride_=2)
self.**conv9** = DoubleConv(64, 32)
self.**conv10** = nn.Conv2d(32, out_ch, 1)
def forward(self, x):
_#print(x.shape)_
c1 = self.**conv1**(x)
p1 = self.**pool1**(c1)
_#print(p1.shape)_
c2 = self.**conv2**(p1)
p2 = self.**pool2**(c2)
_#print(p2.shape)_
c3 = self.**conv3**(p2)
p3 = self.**pool3**(c3)
_#print(p3.shape)_
c4 = self.**conv4**(p3)
p4 = self.**pool4**(c4)
_#print(p4.shape)_
c5 = self.**conv5**(p4)
up_6 = self.**up6**(c5)
merge6 = torch.cat([up_6, c4], _dim_=1)
c6 = self.**conv6**(merge6)
up_7 = self.**up7**(c6)
merge7 = torch.cat([up_7, c3], _dim_=1)
c7 = self.**conv7**(merge7)
up_8 = self.**up8**(c7)
merge8 = torch.cat([up_8, c2], _dim_=1)
c8 = self.**conv8**(merge8)
up_9 = self.**up9**(c8)
merge9 = torch.cat([up_9, c1], _dim_=1)
c9 = self.**conv9**(merge9)
c10 = self.**conv10**(c9)
out = nn.Sigmoid()(c10)
return out
nonlinearity = partial(F.relu, _inplace_=True)
class DecoderBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, n_filters):
super(DecoderBlock, self).__init__()
self.**conv1** = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, in_channels // 4, 1)
self.**norm1** = nn.BatchNorm2d(in_channels // 4)
self.**relu1** = nonlinearity
self.**deconv2** = nn.ConvTranspose2d(in_channels // 4, in_channels // 4, 3, _stride_=2, _padding_=1, _output_padding_=1)
self.**norm2** = nn.BatchNorm2d(in_channels // 4)
self.**relu2** = nonlinearity
self.**conv3** = nn.Conv2d(in_channels // 4, n_filters, 1)
self.**norm3** = nn.BatchNorm2d(n_filters)
self.**relu3** = nonlinearity
def forward(self, x):
x = self.**conv1**(x)
x = self.**norm1**(x)
x = self.**relu1**(x)
x = self.**deconv2**(x)
x = self.**norm2**(x)
x = self.**relu2**(x)
x = self.**conv3**(x)
x = self.**norm3**(x)
x = self.**relu3**(x)
return x
class resnet34_unet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes=1, num_channels=3,pretrained=True):
super(resnet34_unet, self).__init__()
filters = [64, 128, 256, 512]
resnet = models.resnet34(_pretrained_=pretrained)
self.**firstconv** = resnet.**conv1**
self.**firstbn** = resnet.**bn1**
self.**firstrelu** = resnet.**relu**
self.**firstmaxpool** = resnet.**maxpool**
self.**encoder1** = resnet.**layer1**
self.**encoder2** = resnet.**layer2**
self.**encoder3** = resnet.**layer3**
self.**encoder4** = resnet.**layer4**
self.**decoder4** = DecoderBlock(512, filters[2])
self.**decoder3** = DecoderBlock(filters[2], filters[1])
self.**decoder2** = DecoderBlock(filters[1], filters[0])
self.**decoder1** = DecoderBlock(filters[0], filters[0])
self.**decoder4** = DecoderBlock(512, filters[2])
self.**decoder3** = DecoderBlock(filters[2], filters[1])
self.**decoder2** = DecoderBlock(filters[1], filters[0])
self.**decoder1** = DecoderBlock(filters[0], filters[0])
self.**finaldeconv1** = nn.ConvTranspose2d(filters[0], 32, 4, 2, 1)
self.**finalrelu1** = nonlinearity
self.**finalconv2** = nn.Conv2d(32, 32, 3, _padding_=1)
self.**finalrelu2** = nonlinearity
self.**finalconv3** = nn.Conv2d(32, num_classes, 3, _padding_=1)
def forward(self, x):
_# Encoder_
x = self.**firstconv**(x)
x = self.**firstbn**(x)
x = self.**firstrelu**(x)
x = self.**firstmaxpool**(x)
e1 = self.**encoder1**(x)
e2 = self.**encoder2**(e1)
e3 = self.**encoder3**(e2)
e4 = self.**encoder4**(e3)
_# Center_
_# Decoder_
d4 = self.**decoder4**(e4) + e3
d3 = self.**decoder3**(d4) + e2
d2 = self.**decoder2**(d3) + e1
d1 = self.**decoder1**(d2)
out = self.**finaldeconv1**(d1)
out = self.**finalrelu1**(out)
out = self.**finalconv2**(out)
out = self.**finalrelu2**(out)
out = self.**finalconv3**(out)
return nn.Sigmoid()(out)模型实现
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
class double_conv2d_bn(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,in_channels,out_channels,kernel_size=3,strides=1,padding=1):
super(double_conv2d_bn,self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels,out_channels,
kernel_size=kernel_size,
stride = strides,padding=padding,bias=True)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(out_channels,out_channels,
kernel_size = kernel_size,
stride = strides,padding=padding,bias=True)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
def forward(self,x):
out = F.relu(self.bn1(self.conv1(x)))
out = F.relu(self.bn2(self.conv2(out)))
return out
class deconv2d_bn(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,in_channels,out_channels,kernel_size=2,strides=2):
super(deconv2d_bn,self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.ConvTranspose2d(in_channels,out_channels,
kernel_size = kernel_size,
stride = strides,bias=True)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
def forward(self,x):
out = F.relu(self.bn1(self.conv1(x)))
return out
class Unet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Unet,self).__init__()
self.layer1_conv = double_conv2d_bn(1,8)
self.layer2_conv = double_conv2d_bn(8,16)
self.layer3_conv = double_conv2d_bn(16,32)
self.layer4_conv = double_conv2d_bn(32,64)
self.layer5_conv = double_conv2d_bn(64,128)
self.layer6_conv = double_conv2d_bn(128,64)
self.layer7_conv = double_conv2d_bn(64,32)
self.layer8_conv = double_conv2d_bn(32,16)
self.layer9_conv = double_conv2d_bn(16,8)
self.layer10_conv = nn.Conv2d(8,1,kernel_size=3,
stride=1,padding=1,bias=True)
self.deconv1 = deconv2d_bn(128,64)
self.deconv2 = deconv2d_bn(64,32)
self.deconv3 = deconv2d_bn(32,16)
self.deconv4 = deconv2d_bn(16,8)
self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self,x):
conv1 = self.layer1_conv(x)
pool1 = F.max_pool2d(conv1,2)
conv2 = self.layer2_conv(pool1)
pool2 = F.max_pool2d(conv2,2)
conv3 = self.layer3_conv(pool2)
pool3 = F.max_pool2d(conv3,2)
conv4 = self.layer4_conv(pool3)
pool4 = F.max_pool2d(conv4,2)
conv5 = self.layer5_conv(pool4)
convt1 = self.deconv1(conv5)
concat1 = torch.cat([convt1,conv4],dim=1)
conv6 = self.layer6_conv(concat1)
convt2 = self.deconv2(conv6)
concat2 = torch.cat([convt2,conv3],dim=1)
conv7 = self.layer7_conv(concat2)
convt3 = self.deconv3(conv7)
concat3 = torch.cat([convt3,conv2],dim=1)
conv8 = self.layer8_conv(concat3)
convt4 = self.deconv4(conv8)
concat4 = torch.cat([convt4,conv1],dim=1)
conv9 = self.layer9_conv(concat4)
outp = self.layer10_conv(conv9)
outp = self.sigmoid(outp)
return outp
model = Unet()
inp = torch.rand(10,1,224,224)
outp = model(inp)
print(outp.shape)
==> torch.Size([10, 1, 224, 224])相关资源
项目
https://github.com/Andy-zhujunwen/UNET-ZOO?tab=readme-ov-file`
https://github.com/bigmb/Unet-Segmentation-Pytorch-Nest-of-Unetshttps://www.codewithgpu.com/i/bubbliiiing/unet-pytorch/UNet-PyTorch
`
https://huggingface.co/spaces/h2chen/demo_unet
博客
UNet详解(附图文和代码实现)-CSDN博客
<br>
图像分割必备知识点 | Unet详解 理论+ 代码 - 忽逢桃林 - 博客园
